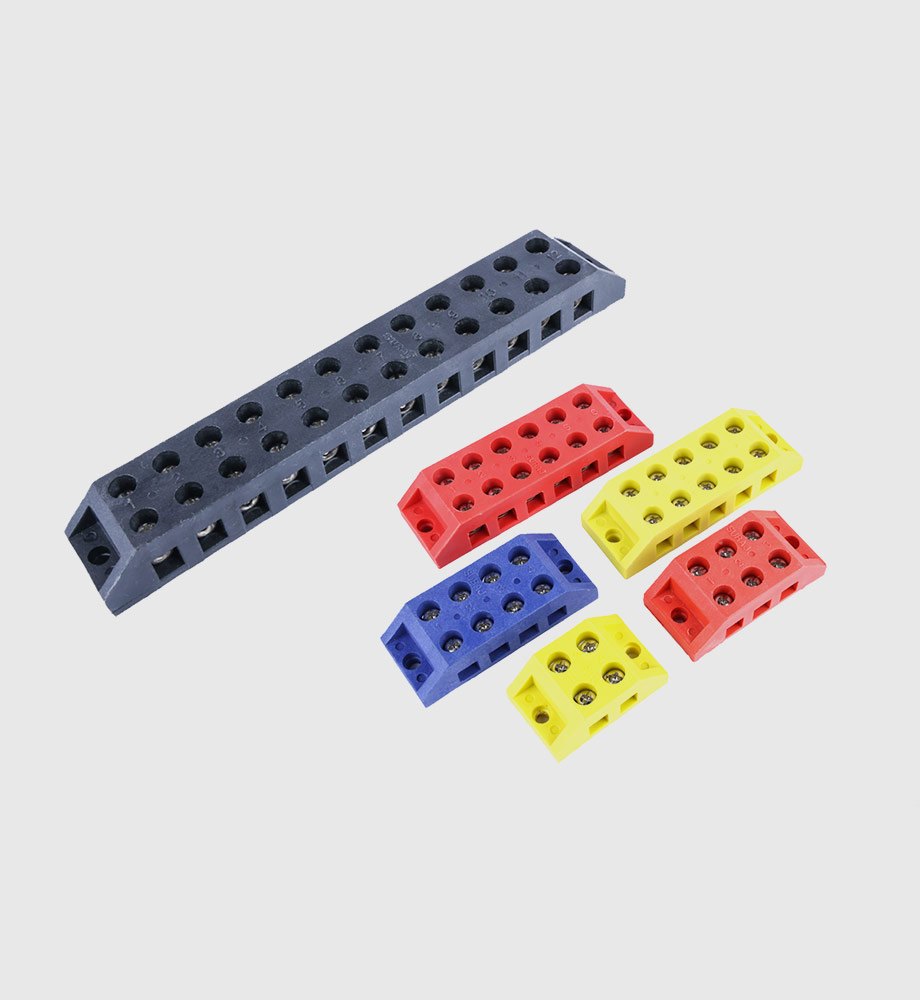
Key Features
- Insulating Body: Typically made from phenol-formaldehyde (Bakelite), PBT or similar high-dielectric plastics. These materials are non-hygroscopic and withstand high voltages.
- Touch-Proof Housing: Enclosed design covers the live terminals for safety.
- Connection Methods: Screw or spring clamp types for fastening copper wires. Some versions incorporate wire entry barriers to prevent shorts.
- Modularity: Blocks can be snapped side-by-side on DIN rails or in modular assemblies.
Benefits
- Safety: Rigid insulating bodies ensure the terminals stay securely in place and reduce risk of fire or short (material is flame-retardant).
- Durability: Phenolic and PBT bases resist cracking and maintain insulation integrity over time.
- Vibration Resistant: Solid mounting prevents loosening in mobile or high-vibration applications.
Applications
- Control Panels: Wiring junctions in automation cabinets, motor control centers, and PLC enclosures.
- Power Distribution: Connecting power and neutral conductors in switchgear and distribution boards.
- Telecom & Data: Organizing twisted pairs or grounding bars in network equipment.
Technical Specifications
- Material: Insulating resin (phenolic or PBT) for the housing; copper or brass conducting parts.
- Voltage Rating: Up to 500–1000 V AC depending on design; PBT parts often rated for high impulse voltages.
- Current Rating: Typically 10–30 A (some heavy-duty versions up to 100 A).
- Certifications: UL/CUL, IEC (often IP20 rated for finger protection).
Unique Selling Points (USPs)
- Premium Insulation: Use of Bakelite and high-grade PBT provides “non-hygroscopic, highly insulating” properties unmatched by lower-grade plastics.
- Universal Compatibility: Many are designed to accept standard ferrules or bootlace crimp terminals for easy wiring.
- Stable Connection: Rigid blocks maintain torque settings and contact pressure over repeated cycles and temperature changes.