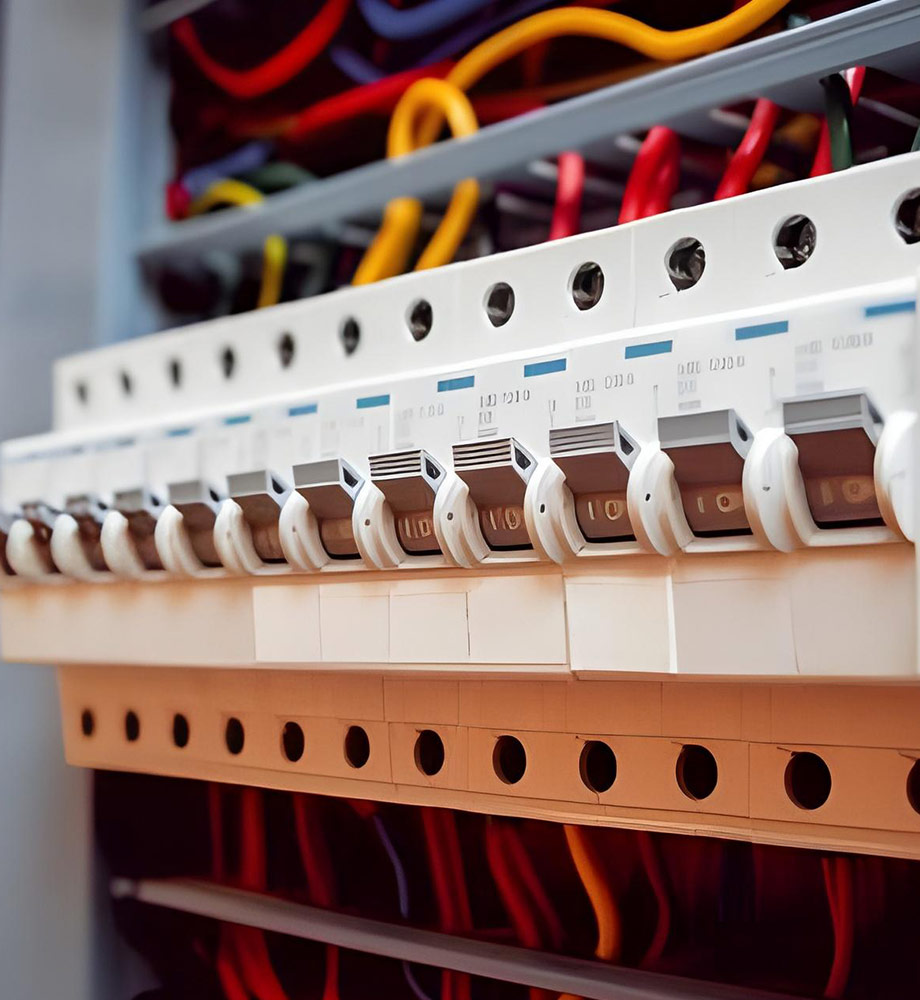
Key Features
- Glass-Polyester Construction: Casings are made from glass-fiber reinforced resin (a thermoset composite). This material provides excellent mechanical strength and electrical insulation.
- Arc-Quenching Design: Internal shape directs arcs into quenching chambers, but the outer housing contains any flashes.
- Flame Resistance: The composite casing is self-extinguishing, meeting UL 94 V0 criteria in many cases.
- Integrated Busway Interface: Often includes molded slots or connections for busbars and panel mounting.
Benefits
- Electrical Isolation: Prevents short circuits between phases and to the ground – the glass-polyester ensures leakage currents are negligible.
- Durability: Resistant to impact and thermal cycling; maintains integrity even under fault conditions.
- Safety: Keeps live contacts safely enclosed; many designs are touch-safe on the outside.
Applications
- Low-Voltage Switchgear: Houses for molded-case circuit breakers (MCCBs) and miniature circuit breakers (MCBs) in electrical panels.
- Motor Control: Enclosures for motor protector breakers in control panels and motor starters.
- Distribution Panels: Main breaker enclosures in switchboards or distribution boxes.
Technical Specifications
- Material: Glass-polyester thermoset (often reinforced with 20–40% glass fiber).
- Voltage Rating: Up to 1000 V in many MCCB designs.
- Standards: Insulation must meet IEC 60695 and UL 489, including impulse and tracking resistance.
- Temperature Range: Typically –40°C to +85°C for standard housings.
Unique Selling Points (USPs)
- Composite Strength: The special glass-resin mix endures electrical arcing stresses and keeps electronics isolated.
- Compact Safety: Enables compact breaker designs by combining structural support and insulation in one molded part.